Security Roles and Permissions allow system administrators to create a standard grouping of permissions that can be assigned to users, and these roles determine what individual users can access and do within the system. Security roles are important because they enable an organization to grant certain people access to certain data and also restrict access to certain data.
| Managing Security Roles | Additional Information | Training and Troubleshooting Resources | ||
|
An example of using security roles is an organization that wants managers to view nearly all data about their direct reports; however, managers should not be allowed to see all data for all employees in the organization. An HR manager may need to see personal or compliance data that is restricted to only HR professionals.
To allow for better control of an administrator's access within the system, individual user's rights are controlled in Security Role Administration.
In addition to controlling access to data, security roles enable an organization to restrict access to functionality, such as administrator settings and the appearance of the Welcome Page.
A security role can be created for different functional roles within an organization, and each role may have different sets of permissions.
To access Security Role Administration, go to .
| PERMISSION NAME | PERMISSION DESCRIPTION | CATEGORY |
| Security Administration - General Constraints | Grants access to apply general constraints to permissions when creating/editing a security role. This permission works in conjunction with the Security Administration - Manager permission. This is an administrator permission. | Core Administration |
Troubleshooting
For use cases that demonstrate how permission constraints are calculated when a user's permission constraints are merged between multiple roles or permissions, See Permission Constraint Calculation Use Cases.
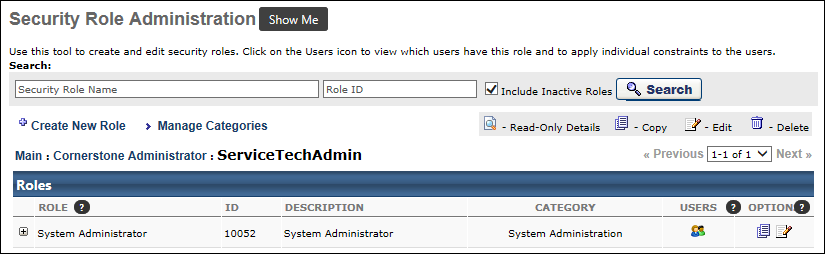
Search for a Security Role
Using the fields in the Search section, administrators can search for a security role by security role name or by security role ID.
- Security Role Name - Enter a role name to search for an existing security role by name.
- Role ID - Enter a role ID to search for an existing security role by security role ID.
- Include Inactive Roles - Select this option to include security roles that have been made inactive in your search results.
After entering the appropriate search criteria, select the button.
Create New Role
Select the Create New Role link to create a new security role. See Security Role - Create.
Manage Security Role Categories
Select the Manage Categories link to manage security role categories. See Add Security Role Categories.
Security Roles Table
The Security Roles table displays existing security roles. Security roles have a parent/child hierarchy, similar to the organizational unit (OU) parent/child hierarchy. Select the Expand icon ![]() next to a security role name to view subordinates security roles. This option is only available for security roles with child roles.
next to a security role name to view subordinates security roles. This option is only available for security roles with child roles.
Add or Remove Users in Security Role
Select the Users icon ![]() next to a role to view names and ID's of users included in this existing security role. Administrators can also add or remove users from a role.
next to a role to view names and ID's of users included in this existing security role. Administrators can also add or remove users from a role.
The Add Users icon is only available for security roles that are not system-defined, such as the Manager role. Any security role that is system-defined is automatically managed by the system. For example, a user is automatically added to the Manager role if they are listed in the Manager role for at least one user. Users cannot be manually added to the Manager role from Security Role Administration.
See Add or Remove Users in a Security Role.
Options
The following options are available for security roles:
- View Details - Click this icon to view a read-only view of the security role.
- Copy - Click this icon to begin copying an existing security role. See Security Role - Create.
- Edit - Click this icon to edit a security role. There are certain behaviors to be aware of when editing a security role. See Modify Security Role.
Major Key Points
- Security Roles are in a hierarchy with the role titled System Administrator at the root. The System Administrator security role is important because it is contains all system permissions. At least one person in the organization must be in this role. All permissions and security roles will derive from this one role.
- Child roles are always a subset of the permissions of the parent role.
- When adding a permission to a child role, it automatically adds the permission to the parent if not already there.
- The constraints may differ, but a parent must always include all the permissions of all of its children.
- When a permission is added to a child role, the permission appears gray in the parent role. This prevents removal of a permission at the parent level that exists in one or more children.
- To remove a permission from the parent, you must first remove it from all the child roles.
- Roles may contain general constraints that are relative to the user; for example, a role may contain a permission with the constraint "Restrict to user's division". However, individual users may have specific constraints such as "Restrict to the Main Division."
- Roles may be marked as dynamic for a group of users or an organizational unit so that every time a user joins that group they will automatically receive the role. Alternatively, if a user leaves that group, they will automatically lose the role.
- Roles can be delegated or shared if the preference is enabled.
Benefits
- Increased security with information.
- Focused Reporting Areas - Results in reports will be limited based on user's constraints to their permissions.
- Roles can be delegated; responsibilities are constrained to the user's organizational unit.
- The option to delegate a role can be turned on or off by availability. For example, if the ILT Facility Owner role was made available to a location, you will have an option available to allow users to delegate this role.
- Multiple constraints and permissions can be applied to a permission and role respectively.
Key Terms
- Role - This is a standard grouping of permissions that can have constraints. A role can be dynamically assigned to an organizational unit or user.
- Permission - This provides a user access to specific functionality within the system. This is also known as a "Right."
- Constraint - This limits a user's permission to a specified area. A constraint can be general to the permission or specific to the user's Division. For example, if a permission grants access to a particular report, a constraint could be added to limit the report results to a particular division.
- Dynamically Assign - This option allows a role to be automatically assigned or removed when a user joins or leaves an organizational unit. A dynamically assigned role is given to a user based on certain actions occurring within a module or based on general system workflows, such as becoming a manager with direct reports in the system. Once the user has been assigned one of these roles, they will receive the role upon the next time they log in to the system. See Add or Remove Users in a Security Role.
- Delegate - This allows users to delegate their role to a user in their organizational unit. Users in this role will see a link to Delegate their rights from the Admin Configuration Tools page (if the user has access to this page). See Add or Remove Users in a Security Role.
Default Dynamically Assigned Security Roles
In addition to the System Administrator role, the following Dynamically Assigned Roles are available:
- Approver - This user is responsible for approving training. This role is automatically assigned to a user when they are listed as another user's approver in the user record. See User Record - Organization Structure.
- Cost Center Approver - This user is responsible for approving training.
- Default Role for Every User in the System - This is a basic user in the system. This role is automatically assigned to a user when they are added to the system.
- Instructor - This role is automatically assigned to a user when they are made an instructor in the system through the ILT functionality.
- Manager - This user is responsible for approving training and maintaining performance-related information on direct reports. This role is automatically assigned to a user when they are listed as another user's manager in the user record. By default, some manager permissions are automatically constrained to Self and Subordinates while others are automatically constrained to Subordinates only. It is important to note that if any permission in the Manager security role is constrained to subordinates (e.g., Self and Subordinates, Subordinates), then this includes all direct and indirect subordinates and this cannot be changed. Applying the Direct Subordinates constraint to a permission in this role that is automatically constrained to subordinates DOES NOT result in the manager being constrained to direct subordinates only.
Best Practices
Knowledge Bank: Security Roles, Permissions, and Constraints Frequently Asked Questions
The following best practices apply to creating and managing security roles:
- The easiest way to add security roles to individuals as they are getting hired into the organization is to dynamically assign the security roles to OUs or groups. When users are automatically added or removed from a group based on the group criteria, they will automatically be assigned or unassigned the relevant security roles. See Use Groups to Assign Security Roles.
- Only add the permissions that are necessary for the role being created. Never replicate permissions that already exist in the default user role.